| dc.contributor.author | Bisaillon, M | fr_FR |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2012-08-30T12:34:37Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2012-08-30T12:34:37Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2001 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.citation | Bisaillon, M, La structure-coiffe des ARN messagers., Med Sci (Paris), 2001, Vol. 17, N° 3; p.312-9 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/1918 | |
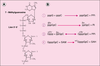
| dc.description.abstract | Les ARN messagers (ARNm) des cellules eucaryotes subissent
d’importantes modifications avant d’être ultérieurement
traduits en protéines. Ainsi, l’ajout d’une structure-coiffe à
l’extrémité 5’ des ARNm augmente considérablement la stabilité
de ces molécules et promeut également une initiation
efficace de la synthèse protéique. Les enzymes responsables
de la synthèse de cette structure ont maintenant été identifiées
chez de nombreux organismes. La caractérisation de
ces protéines de diverses origines nous permet désormais
d’envisager le développement d’inhibiteurs spécifiques ayant
des applications thérapeutiques importantes pour empêcher
le développement de certains agents pathogènes. | fr |
| dc.description.abstract | Recent discoveries about signalling via G protein-coupled receptors have revealed the complexity of this process. Two key factors contribute principally to this complexity: the possibility that one single receptor subtype may govern multiple effector pathways, and the fact that a receptor subtype may be expressed as a mutant form, or an isoform, due to alternative splicing and RNA editing of the transcript. Whereas it is well established that different agonists do not necessarily elicit the same magnitude of response, it is likely that different ligands may also select between several potential signal transduction pathways. The diversity of receptor signalling via a single receptor subtype may be a consequence of specific agonist: receptor: G protein interactions. A better understanding of the activation state(s) of the G protein-coupled receptor appears to be essential in order to develop new ligands, which may either enhance, attenuate, block or reverse a response mediated by a given receptor: effector pathway. Future efforts should not be limited to the study of a receptor under normal conditions, but also to its behaviour under pathophysiological conditions. Particularly, further investigation is required to understand the relevance of the recently discovered receptor isoforms. | en |
| dc.language.iso | fr | fr_FR |
| dc.publisher | Masson, Paris | fr_FR |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [revue papier, ISSN : 0767-0974], 2001, Vol. 17, N° 3; p.312-9 | fr_FR |
| dc.title | La structure-coiffe des ARN messagers. | fr |
| dc.title.alternative | The mRNA cap structure. | fr_FR |
| dc.type | Article | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Molecular Biology Program Sloan-Kettering Institute 1275 York Avenue, Box 73 New York, NY, USA, 10021 | - |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.4267/10608/1918 | |