| dc.contributor.author | Guilhou, J.J. | fr_FR |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2013-02-18T16:18:03Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2013-02-18T16:18:03Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 1993 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.citation | Guilhou, J.J., Pathogénie du psoriasis, Med Sci (Paris), 1993, Vol. 9, N° 4; p.412-416 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/2934 | |
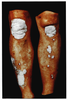
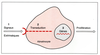
| dc.description.abstract | Psoriasis is characterized by epidermal hyperplasia associated with altered keratinocyte maturation and inflammatory phenomena. Keratinocyte proliferation might be due to extrinsic proliferative signals possibly delivered by various cells, including fibroblasts and lymphocytes. However, many abnormalities of transduction systems have been described, indicating the occurrence of some intrinsinc defect of the psoriatic keratinocyte. Finally psoriasis is a genodermatosis and the recent progresses in molecular biology techniques might help us to determine the genes involved in the disease. | fr |
| dc.language.iso | fr | fr_FR |
| dc.publisher | John Libbey Eurotext, Montrouge | fr_FR |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [revue papier, ISSN : 0767-0974], 1993, Vol. 9, N° 4; p.412-416 | fr_FR |
| dc.title | Pathogénie du psoriasis | fr |
| dc.type | Article | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.4267/10608/2934 | |