| dc.contributor.author | Fantini, J. | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Yahi, N. | fr_FR |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2013-02-18T16:18:55Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2013-02-18T16:18:55Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 1993 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.citation | Fantini, J. ; Yahi, N., Le galactosyl céramide - un nouveau récepteur pour le virus de l'immunodéficience humaine (VIH), Med Sci (Paris), 1993, Vol. 9, N° 8-9; p.891-900 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/3009 | |
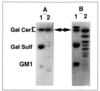
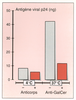
| dc.description.abstract | HIV infects lymphocytes and macrophages that express CD4, a 55 kDa cell surface glycoprotein. However, the ability of HIV to infect CD4-negative cells suggests the existence of an alternate, non-CD4 receptor for the virus, Recently, a glycosphingolipid called galactocerebroside or galactosyl ceramide (GalCer) was proposed as a candidate HIV-1 receptor in neural cells and in colon epithelial cells. Gp120, the external envelope glycoprotein of HIV-1 that recognizes CD4, is involved in the interaction with GalCer. The viral glycoprotein binds also to the sulfated derivative of GalCer, but totally ignores closely related molecules such as glucosyl and lactosyl ceramide. HIV infection of GalCer+/CD4- cells is efficiently inhibited by anti-GalCer monoclonal antibodies. These findings should be important in view of the development of new anti-HIV strategies, especially for the prevention of HIV transmission and pathogenesis in the gastrointestinal mucosa. | fr |
| dc.language.iso | fr | fr_FR |
| dc.publisher | John Libbey Eurotext, Montrouge | fr_FR |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [revue papier, ISSN : 0767-0974], 1993, Vol. 9, N° 8-9; p.891-900 | fr_FR |
| dc.title | Le galactosyl céramide - un nouveau récepteur pour le virus de l'immunodéficience humaine (VIH) | fr |
| dc.type | Article | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.4267/10608/3009 | |