| dc.contributor.author | Albagli, O | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Laget, MP | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Chanut, T | fr_FR |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2012-07-11T08:41:06Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2012-07-11T08:41:06Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 1997 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.citation | Albagli, O ; Laget, MP ; Chanut, T, Neurogenèse et diversification de photorécepteurs de la drosophile., Med Sci (Paris), 1997, Vol. 13, N° 2; p.184-91 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/334 | |
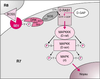
| dc.description.abstract | La différenciation du photorécepteur R7 de la rétine de drosophile
dépend de l’activation du récepteur à domaine tyrosine
kinase (RTK) Sevenless : en l’absence de Sevenless ou de
ses effecteurs, le précurseur R7 adopte un destin non neural,
l’activation ectopique de la cascade Sevenless transforme des
cellules non neurales en R7. La dissection génétique et moléculaire
de la transmission du signal neuralisant enclenché par
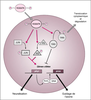
Sevenless a révélé des interactions complexes entre la voie
Ras/Raf/MAPKK/MAPK et d’autres effecteurs cytoplasmiques,
et montré comment le signal Sevenless modifie
l’équilibre entre deux facteurs de transcription antagonistes à
domaine ETS, Yan et PointedP2. La spécification des autres
photorécepteurs ne dépend pas de Sevenless, mais requiert
des facteurs de transcription spécifiques, tels Rough ou
Seven-up. Cependant, les effecteurs de Sevenless sont utilisés
pour la différenciation de la plupart des autres cellules de la
rétine, et contrôlés, dans ce cas, par un autre RTK, Der (Drosophila
EGF-receptor). La diversification des cellules de la
rétine requiert donc l’interprétation distincte d’un même
signal RTK. L’intensité variable du signal RTK, mais aussi
« l’âge» des cellules indifférenciées au moment de sa réception pourraient conditionner le choix d’une destinée. | fr |
| dc.description.abstract | Differentiation of the R7 photoreceptor in the drosophila retina depends upon activation of the tyrosine kinase receptor (RTK) Sevenless (Sev). In the absence of Sev or of its mediators, the R7 precursor adopts a non-neural fate, whereas ectopic activation of the Sev cascade transforms non-neural cells into R7. Genetic and molecular studies of these transformations have allowed the dissection of a neuralizing signal initiated by a RTK. These studies reveal complex interactions between the Ras/Raf/MAPKK/MAPK pathway and other cytoplasmic factors, and show how the Sev signal controls the balance between Yan and PointedP2, two antagonistic ETS transcription factors. Specification of the other photoreceptors does not depend upon Sev, but requires specific transcription factors including Rough and Seven-up. Nevertheless, mediators of Sev are involved in the differentiation of most other retinal cells where they respond to another RTK, the Drosophila EGF receptor Der. To adopt their diverse fates, retinal cells must therefore interpret in distinctive ways the same RTK signal. The choice of their fate could be conditioned by variations in the intensity of the RTK signal, but also by their own developmental age at the time they receive it. [References: 33] | en |
| dc.language.iso | fr | fr_FR |
| dc.publisher | Masson, Paris | fr_FR |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [revue papier, ISSN : 0767-0974], 1997, Vol. 13, N° 2; p.184-91 | fr_FR |
| dc.title | Neurogenèse et diversification de photorécepteurs de la drosophile. | fr |
| dc.title.alternative | Photoreceptor differentiation in Drosophila : transduction and interpretation of the RTK signaling pathway : French-speaking scientists in the United States | fr_FR |
| dc.type | Article | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Inserm U. 124, IRCL, place de Verdun, 59045 Lille, France; UCSF, Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, San Francisco, California 94143-0554, United States; EGCRC, San Francisco General Hospital, Building 1, Room 101, San Francisco, CA 94110, United States | - |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.4267/10608/334 | |