| dc.contributor.author | Chuong Nguyen, Minh Vu | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Lardy, Bernard | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Paclet, Marie-Hélène | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Rousset, Francis | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Berthier, Sylvie | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Baillet, Athan | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Grange, Laurent | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Gaudin, Philippe | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Morel, Françoise | - |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2018-05-30T11:35:53Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2018-05-30T11:35:53Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2015 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | Chuong Nguyen, Minh Vu ; Lardy, Bernard ; Paclet, Marie-Hélène ; Rousset, Francis ; Berthier, Sylvie ; Baillet, Athan ; Grange, Laurent ; Gaudin, Philippe ; Morel, Françoise ; Les NADPH oxydases, Nox : Une nouvelle famille d’isoenzymes, Med Sci (Paris), 2015, Vol. 31, N° 1 ; p. 43-52 ; DOI : 10.1051/medsci/20153101012 | |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/8547 | |
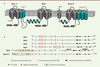
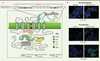
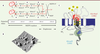
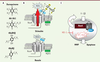
| dc.description.abstract | La famille des NADPH oxydases, Nox, chez l’homme, est composée de sept isoenzymes, cinq Nox et deux Duox (dual oxidase). Leur unique fonction est de réduire l’oxygène moléculaire pour synthétiser l’anion superoxyde et les espèces radicalaires, ROS (reactive oxygen species), qui en découlent. Les ROS sont produites en excès dans les maladies chroniques et les pathologies du vieillissement. La compréhension des mécanismes impliqués dans le fonctionnement des Nox, et l’émergence d’inhibiteurs spécifiques, imposent une connaissance approfondie de leur nature et de leur structure. Les objectifs de cette revue sont de mettre l’accent, dans une approche structure/fonction, sur les principales propriétés qui rassemblent et différencient les Nox chez l’homme. | fr |
| dc.description.abstract | NADPH oxidases, Nox, are a family of isoenzymes, composed of seven members, whose sole function is to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS). Although Nox catalyze the same enzymatic reaction, they acquired from a common ancestor during evolution, specificities related to their tissue expression, subcellular localization, activation mechanisms and regulation. Their functions could vary depending on the pathophysiological state of the tissues. Indeed, ROS are not only bactericidal weapons in phagocytes but also essential cellular signaling molecules and their overproduction is involved in chronic diseases and diseases of aging. The understanding of the mechanisms involved in the function of Nox and the emergence of Nox inhibitors, require a thorough knowledge of their nature and structure. The objectives of this review are to highlight, in a structure/function approach, the main similar and differentiated properties shared by the human Nox isoenzymes. | en |
| dc.language.iso | fr | |
| dc.publisher | Éditions EDK, Groupe EDP Sciences | |
| dc.relation.ispartof | M/S Revues | |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [ISSN papier : 0767-0974 ; ISSN numérique : 1958-5381], 2015, Vol. 31, N° 1; p. 43-52 | |
| dc.subject.mesh | Animaux | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Évolution moléculaire | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Humains | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Isoenzymes | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Thérapie moléculaire ciblée | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Famille multigénique | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Conformation des protéines | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | composition chimique | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | génétique | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | métabolisme | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | tendances | fr |
| dc.title | Les NADPH oxydases, Nox : Une nouvelle famille d’isoenzymes | fr |
| dc.title.alternative | NADPH oxidases, Nox: new isoenzymes family | en |
| dc.type | Article | |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | GREPI (groupe de recherche et d’étude du processus inflammatoire), université Joseph Fourier, Grenoble, France | |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | EFS Rhône-Alpes, 29, avenue des Maquis du Grésivaudan, 38700 La Tronche, France | |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | DBTP (département de biochimie, toxicologie et pharmacologie), institut de biologie et pathologie, CHU de Grenoble, France | |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Clinique universitaire de rhumatologie, Hôpital Sud, CHU de Grenoble, France | |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1051/medsci/20153101012 | |
| dc.identifier.pmid | 25658730 | |