| dc.contributor.author | Ji, Shu-meng | - |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2019-11-05T12:51:45Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2019-11-05T12:51:45Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2018 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | Ji, Shu-meng ; Overexpression of SLC25A15 is involved in the proliferation of cutaneous melanoma and leads to poor prognosis, Med Sci (Paris), , Vol. 34, N° HS ; p. 74-80 ; DOI : 10.1051/medsci/201834f113 | |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/9990 | |
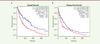
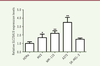
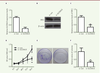
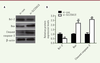
| dc.description.abstract | Melanoma is a skin tumor with a high degree of malignancy, poor prognosis and few effective therapies. Deprivation of the arginine from cancer cells through transport inhibition and arginine depletion is a novel strategy for cancer therapy. In this study, we have investigated the effect of SLC25A15, which encodes the mitochondrial ornithine carrier 1, on melanoma progression. Using bioinformatics methods to screen the data from TCGA and GEO, we found that SLC25A15 is overexpressed in patients with melanoma and negatively related with the overall and disease-free survival rates. Knockdown the expression of SLC25A15 by siRNA could effectively inhibit the proliferation of A375 melanoma cells, as detected by CCK8 and colony formation. Furthermore, SLC25A15 siRNA was able to promote apoptosis of A375 cells, which exhibited decreased expression levels of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 while showing increased pro-apoptotic protein Bax and cleaved caspase-3. All these results suggest that the overexpression of SLC25A15 is involved in the progression of melanoma and may predict the prognosis of melanoma. This may shed new lights on the diagnosis and therapy of melanoma in the future. | en |
| dc.language.iso | en | |
| dc.publisher | EDP Sciences | |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [ISSN papier : 0767-0974 ; ISSN numérique : 1958-5381], , Vol. 34, N° HS; p. 74-80 | |
| dc.title | Overexpression of SLC25A15 is involved in the proliferation of cutaneous melanoma and leads to poor prognosis | en |
| dc.type | Article | |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Department of Dermatology, the People’s Hospital of Xintai, No.1329 of Xinfu Road, Xintai 271200, Shandong, P.R. China | |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1051/medsci/201834f113 | |