| dc.contributor.author | Muller, M | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Berwaer, M | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Caccavelli, L | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Manfroid, I | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Nalda, A | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Pendeville, H | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Pernasetti, F | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | van de Weerdt, C | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Peers, B | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Martial, JA | fr_FR |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2012-08-23T07:50:52Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2012-08-23T07:50:52Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 1998 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.citation | Muller, M ; Berwaer, M ; Caccavelli, L ; Manfroid, I ; Nalda, A ; Pendeville, H ; Pernasetti, F ; van de Weerdt, C ; Peers, B ; Martial, JA, Régulation transcriptionnelle du gène de la prolactine humaine., Med Sci (Paris), 1998, Vol. 14, N° 5; p.580-7 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/1096 | |
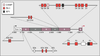
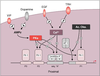
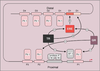
| dc.description.abstract | Le gene humain de la prolactine (hPRL) est exprime essentiellement par l' antehypophyse. L' analyse des elements regulateurs de la transcription sur plus de 5 000 bases en amont du site de debut de transcription a montre l' importance du controle par le facteur de transcription Pit-1, specifique de l' hypophyse, a cote de facteurs ubiquistes. Des hormones modulent l' expression du gene hPRL, transmettant leur signal par les voies intracellulaires de l' AMP cyclique et du calcium, relayees au niveau du promoteur proximal (-250/+1) essentiellement par les facteurs de transcription Pit-1 et AP-1. Les recepteurs nucleaires controlent aussi en partie la transcription de hPRL: le recepteur des oestrogenes l' active en se liant aux elements de reponse distaux ; les recepteurs nucleaires des hormones thyroidiennes et des glucocorticoides la repriment en interferant respectivement avec la fonction activatrice de AP-1 et de Pit-1. | fr |
| dc.description.abstract | The human prolactin gene is mainly expressed in the anterior pituitary under the control of the transcription factor Pit-1. Positive and negative regulatory elements have been identified in the 5'-flanking region of the hPRL gene. Binding sites for the cell-specific factor Pit-1 and for ubiquitous factors were identified in a more than 5000 base pair long upstream region. In addition, prolactin expression is modulated by extra-cellular factors such as dopamine, thyrotropine releasing hormone, thyroid hormone and steroids. Factors acting through signal transduction pathways (cAMP, Ca2+) regulate hPRL expression mainly via the proximal promoter (-250/+1). Protein-kinases and -phosphatases modulate the activation function of transcription factors Pit-1, AP1 and other, binding to their respective sites on the promotor. The estrogen receptor activates hPRL expression by binding to a distal response element, while glucocorticoid and thyroid hormone receptors repress hPRL gene transcription by interfering with the activating function of, respectively, Pit-1 and AP1. In extrapituitary cells, transcription of the hPRL gene is initiated at an alternative, far upstream, site and hPRL expression is controlled by a lymphocyte-specific element. Binding sites for cell-specific and ubiquitous factors were detected in this region. [References: 41] | en |
| dc.language.iso | fr | fr_FR |
| dc.publisher | Masson, Paris | fr_FR |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [revue papier, ISSN : 0767-0974], 1998, Vol. 14, N° 5; p.580-7 | fr_FR |
| dc.title | Régulation transcriptionnelle du gène de la prolactine humaine. | fr |
| dc.title.alternative | Transcriptional regulation of the human prolactin gene | fr_FR |
| dc.type | Article | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Laboratoire de biologie moleculaire de genie genetique, Universite de Liege, Institut de chimie B6, 4000 Sart-Tilman, Belgium; Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Mereside 8AF25, Aderley Park, Cheshire SK10 4TG, United Kingdom; Inserm U. 430, Laboratoire d'immunopathologie, Hopital Broussais, 96, rue Didot, 75014 Paris, France; Laboratoire d'embryologie moleculaire et experimentale, Universite Paris XI, Centre d'Orsay, Batiment 445, 91405 Orsay, France; Department of biochemistry, St Jude Children's Research Hospital, 332, North Lauderdale, Memphis, TN 38105-2794, United States; Department of reproductive medicine, 9500 Gilman Dr, University of California, La Jolla, San Diego, CA 92093-0674, United States | - |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.4267/10608/1096 | |