| dc.contributor.author | Georget, V | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Nicolas, JC | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Sultan, C | fr_FR |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2012-08-23T13:55:14Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2012-08-23T13:55:14Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 1999 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.citation | Georget, V - Nicolas, JC - Sultan, C, La green fluorescent protein : application à la dynamique intracellulaire des récepteurs stéroïdiens., Med Sci (Paris), 1999, Vol. 15, N° 1; p.45-55 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/1195 | |
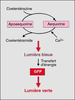
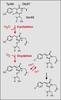
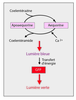
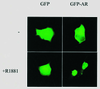
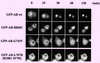
| dc.description.abstract | La green fluorescent protein (GFP) est une proteine extraite de la meduse Aequorea victoria. Cette proteine a la particularite d' emettre de la fluorescence sous UV sans l' ajout de substrat ou de co-facteurs. Le clonage de son gene et l' etude de son expression dans des bacteries ou dans des organismes plus complexes tel que C. elegans ont enrichi les perspectives de son application dans la recherche biomedicale. Le gene de la GFP est aujourd' hui utilise comme gene rapporteur, comme marqueur cellulaire ou encore comme marqueur moleculaire. Le gene codant pour la GFP a par exemple ete fusionne aux genes codant pour des recepteurs steroidiens afin de connaitre la dynamique intracellulaire de ces recepteurs. A ce jour, ont ete rapportees les proteines de fusion avec le recepteur des glucocorticoides (GFP-GR), le recepteur des mineralocorticoides (GFP-MR) et le recepteur des androgenes (GFP-AR). La fluorescence emise par la GFP permet de localiser les proteines dans les compartiments cellulaires et d' en definir ainsi les deplacements lors de stimulations diverses, rendant accessible la visualisation d' evenements cellulaires dynamiques. | fr |
| dc.description.abstract | The green fluorescent protein (GFP) comes from the Aequorea victoria jellyfish. In vivo, it acquires the capacity of fluorescence by activation of aequorin. In vitro, it is activated by simple exposure to standard long-wave ultraviolet or blue light. GFP does not require the addition of substrate or cofactors for generation of its green light and it represents a new tool for monitoring the dynamic processes in living cells and organisms. It can produce fluorescence in various organisms, such as bacteria, plants and mammals, GFP is now applied as a reporter for gene expression, as a marker to study cell lineage and as a tag to localize proteins in living cells. GFP does not require cell fixation or other chemical steps for analysis, contrary to immunocytochemistry. Immunodetection needs fixation and permeabilization steps, which may lead to artefacts in the pattern of localization. This would explain particularly the contradictory results about the localization of the steroid receptors. Several studies have thus been developed using GFP tagged to different steroid receptors: glucocorticoid receptor (GR), mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) and androgen receptor (AR). In absence of hormone, GFP-GR and GFP-AR were described to be cytoplasmic, while the GFP-MR was both cytoplasmic and nuclear. In presence of each specific ligand, GFP-steroid receptors were all nuclear. Formation of nuclear clusters were observed in the presence of agonists for GFP-GR and GFP-MR. GFP permits the analysis of dynamic cellular events and has already been etablished as an important tool for many branches of biological research. [References: 67] | en |
| dc.language.iso | fr | fr_FR |
| dc.publisher | Masson, Paris | fr_FR |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [revue papier, ISSN : 0767-0974], 1999, Vol. 15, N° 1; p.45-55 | fr_FR |
| dc.title | La green fluorescent protein : application à la dynamique intracellulaire des récepteurs stéroïdiens. | fr |
| dc.title.alternative | Green fluorescent protein : its application to the study of intracellular dynamics of steroid receptors | fr_FR |
| dc.type | Article | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Inserm U. 439, Pathologie moleculaire des recepteurs nucleaires, 70, rue de Navacelles, 34090 Montpellier, France; Unite BEDR, hopital Lapeyronie, 34295 Montpellier, France; Unite d'endocrinologie pediatrique, Hopital A.-de-Villeneuve, 34295 Montpellier, France | - |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.4267/10608/1195 | |