| dc.contributor.author | Pauloin, A. | fr_FR |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2013-02-18T16:18:56Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2013-02-18T16:18:56Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 1993 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.citation | Pauloin, A., Bréfeldine A, protéines-G et transports membranaires golgiens., Med Sci (Paris), 1993, Vol. 9, N° 8-9; p.917-925 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/3012 | |
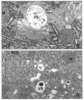
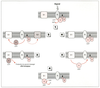
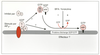
| dc.description.abstract | This review has attempted to provide a synthesis of the growing number of observations on the effects of the fungal metabolite brefeldin A. This drug dramatically alters the morphology of the Golgi complex and the return of Golgi markers to the endoplasmic reticulum. Intercisternal transport in the Golgi complex is mediated by non clathrin coated vesicles, The formation of these vesicles is dependent on the recruitment of a set of proteins from the cytosol, the coatomer. Brefeldin A blocks this step as demonstrated by the redistribution of beta-COP, a component of coatomer, from Golgi to cytosol. In the absence of vesicle formation, Golgi cisternae tend to form tubules which are elongated along microtubules and rapidly fuse with the endoplasmic reticulum. Since all of these changes can be prevented by pretreating intact or permeabilized cells with AlF4- or GTPgammaS respectively (both of which are thought to act by locking G proteins in the active state), the potential role of trimeric G protein and small G protein has been investigated. Current data suggest that the assembly of cytosolic proteins on and off Golgi membranes is a process controlled in part by one or more membrane bound trimeric G proteins and by ARF small G protein family members. Binding of ARF to Golgi membranes is necessary before coatomer can bind these membranes, so the primary effect of BFA seems to be on the reaction responsible for ARF binding. The recent discovery that Golgi membrane can specifically catalyse the exchange of GTP onto ARF and that BFA prevents this function have confirmed this hypothesis. | fr |
| dc.language.iso | fr | fr_FR |
| dc.publisher | John Libbey Eurotext, Montrouge | fr_FR |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [revue papier, ISSN : 0767-0974], 1993, Vol. 9, N° 8-9; p.917-925 | fr_FR |
| dc.title | Bréfeldine A, protéines-G et transports membranaires golgiens. | fr |
| dc.type | Article | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.4267/10608/3012 | |