Répression transcriptionnelle du gène TRH
Date
2005Auteur
Guissouma, Hajer
Dupré, Sandrine M.
Demeneix, Barbara A.
Metadata
Afficher la notice complèteRésumé
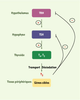
Les hormones thyroïdiennes (HT : T3, T4) exerçant des effets pléiotropes chez les vertébrés, leur synthèse et leur sécrétion doivent être finement contrôlées. Elles agissent elles-mêmes sur leur production, par un système de rétrocontrôle négatif de l’expression des gènes hypothalamique TRH et hypophysaire TSH. Les fondements moléculaires de cette répression transcriptionnelle des gènes TRH et TSH par l’hormone T3, forme biologiquement la plus active des HT, restent méconnus. Certaines caractéristiques de cette régulation commencent toutefois à être identifiées, notamment le rôle spécifique des isoformes TRβ (versus TRα) des récepteurs des HT. La spécificité fonctionnelle de ces isoformes résiderait principalement dans leur extrémité aminoterminale, qui permettrait une interaction différentielle avec certains comodulateurs. L’objectif, aujourd’hui, est de caractériser ces comodulateurs et d’analyser leur contribution à la régulation transcriptionnelle du gène TRH par l’hormone T3. The synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones (TH: T3, T4) must be strictly regulated. TH act on their own production via a negative feedback system. The synthesis of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), produced in the hypothalamus, and thyrotropin (TSH) in the pituitary is inhibited at the transcriptional level by TH. TRH and TSH stimulate production of TH. An outstanding, still open, question is the molecular basis of T3-dependent transcription repression of TRH and TSH genes. However, some regulatory components have been identified, with the β-TH receptor (TRβ) playing a specific regulatory role (versus TRα) in the negative feedback effects of T3 on production of TRH and TSH. Moreover, the N-terminus of TRβ is known to be a key element in this regulation. A hypothesis to explain this isoform specificity could be that TRβ and TRα interact differentially with transcriptional comodulators. Thus, it is critical to characterize these comodulators and to analyse their contribution to the transcription regulation of TRH
Pour citer ce document
Guissouma, Hajer ; Dupré, Sandrine M. ; Demeneix, Barbara A. ; Répression transcriptionnelle du gène TRH , Med Sci (Paris), 2005, Vol. 21, N° 10; p. 854-859 ; DOI : 10.1051/medsci/20052110854



