| dc.contributor.author | An, Xiao-qun | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Xi, Wei | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Gu, Chen-yun | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Huang, Xiao | - |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2019-11-05T12:52:02Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2019-11-05T12:52:02Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2018 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | An, Xiao-qun ; Xi, Wei ; Gu, Chen-yun ; Huang, Xiao ; Complement protein C5a enhances the β-amyloid-induced neuro-inflammatory response in microglia in Alzheimer’s disease, Med Sci (Paris), , Vol. 34, N° HS ; p. 116-120 ; DOI : 10.1051/medsci/201834f120 | |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/9997 | |
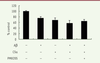
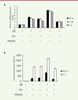
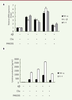
| dc.description.abstract | Objective: The dysregulation of neuro-inflammation is one of the attributes of the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Over-expression of complement proteins co-localizes with neurofibrillary tangles, thereby indicating that a complement system may be involved in neuro-inflammation. Here, we report the influence of complement activation on the neuro-inflammation using a microglial cell line. Methods: first, we performed a cytotoxic assay using the microglial cells BV-2. Second, after treatment of BV-2 cells with Aβ42 and/ or C5a, the anaphylatoxin derived from C5, we determined the expression levels of the pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Finally, we explored whether this neuroinflammatory response was mediated by JAK/ STAT3 signaling. Results: C5a had an enhanced effect on the neural cell viability of BV-2 cells treated with Aβ42. In addition, C5a also increased the Aβ-induced neuro-inflammatory response, and these effects were blocked by the C5aR antagonist, PMX205. Finally, we demonstrated that the neuro-inflammatory responses induced by Aβ and C5a were mediated through JAK/STAT3 signaling. By blocking this pathway with an antagonist, AG490, the expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 was alleviated. Conclusion: The complement protein C5a could exaggerate the Aβ-induced neuroinflammatory response in microglia, and C5aR may be a potential therapeutic tool for AD treatment. | en |
| dc.language.iso | en | |
| dc.publisher | EDP Sciences | |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [ISSN papier : 0767-0974 ; ISSN numérique : 1958-5381], , Vol. 34, N° HS; p. 116-120 | |
| dc.title | Complement protein C5a enhances the β-amyloid-induced neuro-inflammatory response in microglia in Alzheimer’s disease | en |
| dc.type | Article | |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | MD, Department of Psychiatry, Yangpu District Mental Health Center of Shanghai, 585 Jungong Road, Shanghai (200090), China | |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | MD, Department of Psychological Medicine, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, 180 Fenglin Road, Shanghai (200032), China | |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1051/medsci/201834f120 | |