| dc.contributor.author | Darmaun, D. | fr_FR |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2013-02-18T16:18:54Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2013-02-18T16:18:54Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 1993 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.citation | Darmaun, D., Intestin et métabolisme de la glutamine, Med Sci (Paris), 1993, Vol. 9, N° 8-9; p.884-890 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/3008 | |
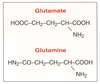
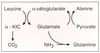
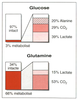
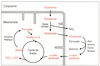
| dc.description.abstract | Although long considered almost exclusively as an absorptive organ, the gut plays a prominent role in the metabolism of glutamine, the most abundant amino acid in the body. The small intestine extracts more than 20 % of whole body glutamine production in most species, and, most likely, humans as well. Glutamine oxidation provides 30-50 % of the energy requirement of the gut, 5 times the contribution of glucose. Glutamine's use as a preferred intestinal fuel seems advantageous in view of : (1) the large (congruent-to 80 g), and continuously replenished (congruent-to 85 g/d) glutamine stores available in the body ; (2) the role of glutamine as a precursor of purines and pyrimidines, the building blocks of nucleic acids, that are in high demand in a tissue with high rates of cell division ; (3) the role of glutamine as a preferred fuel for the gut-associated lymphoid tissue ; and (4) finally, glutamine's potent stimulatory effect on sodium, and water absorption. The multifaceted role of glutamine in the small intestine suggests further evaluation of its potential therapeutic use is warranted. | fr |
| dc.language.iso | fr | fr_FR |
| dc.publisher | John Libbey Eurotext, Montrouge | fr_FR |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [revue papier, ISSN : 0767-0974], 1993, Vol. 9, N° 8-9; p.884-890 | fr_FR |
| dc.title | Intestin et métabolisme de la glutamine | fr |
| dc.type | Article | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.4267/10608/3008 | |